Rainwater Harvesting in Bangalore
Bangalore is blessed with a relatively well distributed rainfall and has a rainfall distribution which is Bi-modal (two peak rainfall seasons in a year). Rainwater Harvesting (RWH) system can be used to recharge the ground water or stored in storage structures for subsequent use. A well planned RWH system can reduce up to 30% of the water requirement from other conventional sources like bore well or municipal supply. The following strategy has been found most suitable for rainwater harvesting implementation in Bangalore.
- Storage of rainwater for direct use: Typically roof areas qualify well for such a strategy. The water from this run-off is first rain separated, filtered and then let into the storage. The water can be used for all household purposes such as washing, cleaning, gardening etc. A water testing process prior to use for drinking and cooking purposes is recommended. Provide a capacity of 0.2 to 0.3 Liters per square meter of the roof area in case the roof is maintained clean.
- Groundwater recharge: In the context of Bangalore, the most effective recharge structure has been found to be a recharge well whose depth is a minimum of around 20 feet. These recharge wells recharge the shallow aquifer. Water needs to be distilled adequately before allowing the water into recharge wells.
Rainfall pattern in Bangalore
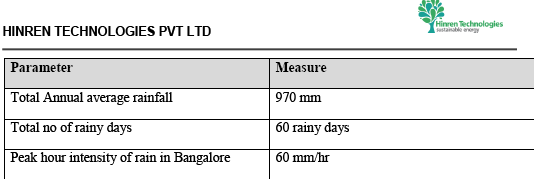
The following are details about the rainfall pattern in Bangalore and form the base assumptions for all designs and calculations:
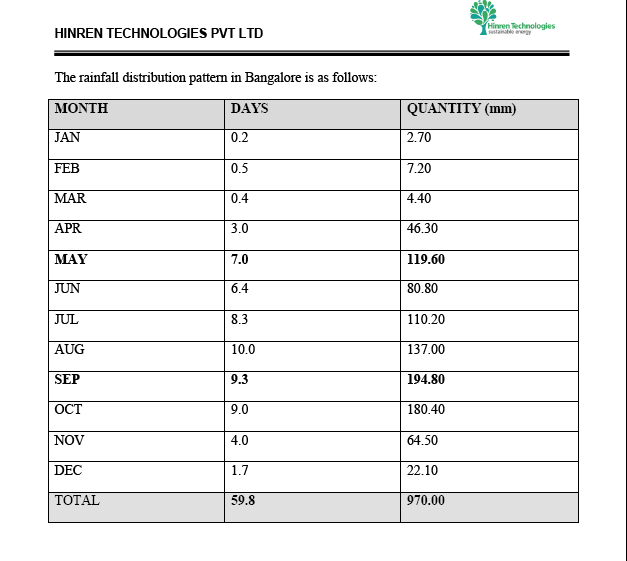
Rainfall distribution pattern in Bangalore
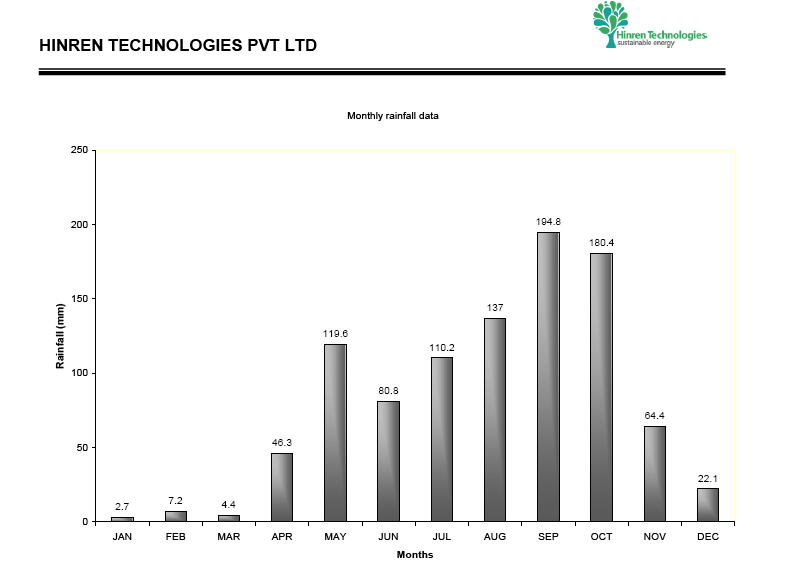
Monthly Rainfall data
Based on the above details the storage structures or recharge structures can be designed for 30 mm rainfall which is optimum and economical storage.
How to calculate the Required Storage or Recharge structure capacity?
- Calculation of Storage volume as per BBMP Regulation: The required storage can also be calculated as per the BBMP regulations. As per the regulation the storage structure should be designed at 20 Litres per square Meter of the roof.
Eg: If the roof area is 100 SqM then the storage or recharge structure capacity will be 100 x 20 = 2000 Ltrs
- Calculation of storage / recharge volume based on the average rain fall: The storage or Recharge structure capacity can be calculated by the amount of runoff from your roof taking into consideration the losses due to evaporation, leakages etc. The optimum storage = Roof Area in SqM x Runoff Co-Efficient (0.9) x Average Rainfall in mm, where Runoff co-efficient is the percentage of water from the roof that comes down in the rainwater pipes which is taken as 90% as about 10% will be lost by evaporation, leakages etc.
Average Rain fall of Bangalore can be taken as 30mm. Eg: If the roof area of a building is 100 SqM then the storage or recharge structure capacity will be 100 x 0.9 x 30 = 2700 Litres