RBI Reduces Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate To Safeguard Economy From COVID-19 Impact
Key Highlights:
- RBI cuts Repo Rate by 75 basis points to 4.4%
- Reverse Repo Rate by 90 basis points to 4%
- CRR cuts from 4% to 3% for all banks for a period of one year
- He also permits all lending Banks, HFCs, and NBFCs to allow a 3-month moratorium on payment of installments on term loans.
- Rs 3.74 lakh crore liquidity to be injected into the system
On 27th March 2020, just a day after Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced massive Rs 1.7 trillion economic packages for the nation, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governor Shaktikanta Das in its 8th Bi-monthly Monetary Policy Statement, 2019-2020 announced BIG-BANG steps cutting lending rates by lowering repo rate and reverse repo rate by huge 70 bps and 90 bps respectively. He also announced a 3-month moratorium on loans and a 100 bps cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) to bring more liquidity in the system. This move by RBI will inject liquidity of Rs 3.74 lakh crore to the system and at the same time, de-stress the impact from 21-days lockdown.
These BIG-BANG moves which were earlier scheduled for 31st March to 3rd April came early as RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to advanced its meetings seeing the Coronavirus crisis and voted for a massive reduction in repo rate to ease economic risks.
RBI’s Repo rate is the key interest rate at which the RBI lends funds to commercial banks while Reverse repo rates is the rate at which RBI borrows money from commercial banks to set the floor of the liquidity adjustment facility corridor.
The interest rate cut to the 75 bps, which brings to repo rate down to 4.4% from 5.15%. At the same time, the reverse repo rate has also been reduced by 90 bps to 4%.
Hence, the repo rate has dropped to the lowest ever. Before this, it had hit the lowest point of 4.74% in April 2009 during the Global Financial Crisis.
How Repo Rate (%) Changed 8th Times In A Year
| Date & Year | Reduced % |
| 6th February 2019 | 6.25 |
| 4th April 2019 | 6 |
| 6th June 2019 | 5.75 |
| 7th August 2019 | 5.40 |
| 4th October 2019 | 5.15 |
| 5th December 2019 | 5.15 |
| 6th February 2020 | 5.15 |
| 27th March 2020 | 4.40 |
| 22nd May 2020 | 4 |
To ease the pressure on people who were staring at loan defaults, RBI asked banks to announce a 3-month pause on all EMIs.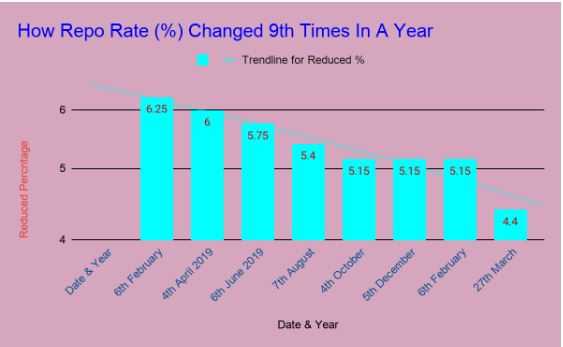
He further added that macroeconomic fundamentals are stronger than the 2008 financial market crisis and take the country in confidence saying that the banking system in India is safe, their deposits are safe in private banks, so, the public should not create a situation like panic withdrawal.
Meta Description: The RBI has allowed banks to provide a 3-month moratorium on loans and EMI repayments. It has also slashed the key repo rate by 75 basis points to 4.4% in order to strengthen growth as India fights Coronavirus (Covid-19).
RBI’s Repo Rate Update:
On 22nd of May 2020, RBI Governor Shaktikant Das held a press conference and reduced the Repo Rate by 40 BPS. Below measures have been taken by RBI:
RBI Monetary Policy Update 2020
The Key Indicators With Their Current Rates
| INDICATOR | CURRENT RATE |
| Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) | 3% |
| Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) | 18.50% |
| Repo Rate (RR) | 4% |
| Reverse Repo Rate (RRR) | 3.35% |
| Marginal Standing Facility Rate (MSFR) | 4.65% |
| Bank Rate (BR) | 4.65% |
40 BPS Repo Rate Cut
Repo rate decreased to 4% from 4.4% in the off-cycle meeting. Reverse repo rate stood at 3.35%
Accommodation stand till growth revive
MPC voted in a 5:1 ratio for a rate cut and will continue with accommodative stand till growth revive.
Domestic Development
High-frequency indicators saw a huge collapse, both in urban and rural front. Merchandise exports plunged 60.3%, imports contracted by 58.6% in April 2020. Consumer durable production declined by 33% in March 2020.
Silver Lining
Agriculture and allied activities a hope from the normal south-west monsoon this year.
Inflation
Food inflation surged in April 2020 to 8.6% with vegetables, oilseeds, and milk being the pressure points.
Outlook
- Inflation highly uncertain and headline inflation in H1FY21 will stay intact but by Q3 and Q4 it may fall below the target of 4%.
- GDP is likely to remain in negative territory in FY21. However, we will see a gradual revival of activities and demand by the 2nd half of FY21.
Regulatory and Development
- In order to give greater flexibility of SIDBI, another 90 days moratorium period for the 90 days term loan facilities will be offered.
- The facility of Rs 15,000 crore line of credit for 90 days for US dollar swap facility will be given to EXIM Bank. This will have a rollover facility for up to one year.
- The loan moratorium will be extended to 31st August 2020. Lending institutions are being permitted to restore the margins for working capital to the origin level by March 31st, 2021.
- The maximum permitted period of pre and post-shipment of credit increased from 1 year to 15 months.
- Extension of time-period for outward payments for normal imports from 6 months to 12 months.
- The group exposure limit of banks will be increased from 25% to 30%.
- The voluntary holding route for FPIs extended for 3 months.








